
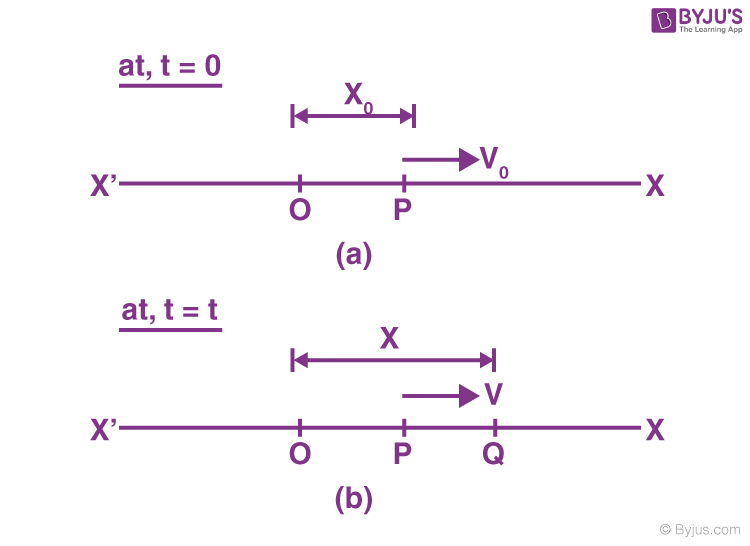
This system is called the simple harmonic oscillator, and the associated motion is called simple harmonic motion. Where the amplitude A and phase &varphi depends on the initial velocity and position of the mass at the time of release. If an object of mass m is attached to the end of the spring, extended and then released (possibly with a nonzero initial velocity), it will oscillate periodically according to the formula: The constant of proportionality, k, is known as the spring constant :

Hooke's Law states that the force F exerted by a stretched spring is proportional to its displacement, x, from the equilibrium position. "The career of a young theoretical physicist consists of treating the harmonic oscillator in ever-increasing levels of abstraction"


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
